Entry Into Telecommunications: Rural ILEC Perspective
The views and opinions expressed in this submission are solely those of the authors and do not represent the views of the Department of Justice.
Slide 1

Entry into Telecommunications
Rural ILEC Perspective
Jill Canfield
Senior Regulatory Counsel
NTCA
jcanfield@ntca.org
Slide 2
Changing Face of Telecommunications

Slide 3
Rural Youth
- 9 out of 10 have mobile phone
- Pay up to $50/month for service
- Consider mobile service “essential”
- 90% have Internet connection
- Primary use is email
- Consider broadband access “essential”
- Half have more than 100 channels of video
- No brand loyalty
Slide 4
Independent Rural Carriers
- Independent Rural carriers are progressive:
- Rural telephone companies were the first to deploy digital switching
- 97% offer custom calling features
- 92% offer Internet
- 84% offer long distance
- 55% offer mobile wireless service
- 29% are CLECs
- Rural Carriers are community based companies with local decision making
- Rural Carriers are strongly committed to public service
- Rural Carriers have a reputation for quality service
Slide 5
Slide 6
Advancing the Communications Revolution
Copyright MapInfo Corp
1999 All Rights Reserved
Slide 7
Competitive Pressures
- Minutes of use declining
- Increased emphasis on broadband “pipe”
- 87% face broadband competition from at least one other provider
- Most face competition only in cities and towns, but 47% throughout service territory
- 54% “very concerned” about cable offering voice
Slide 8
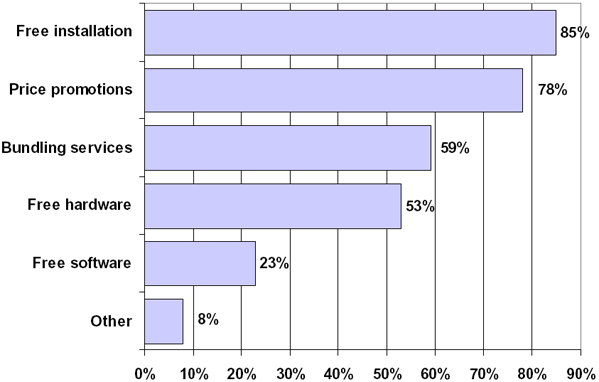
BROADBAND MARKETING PROMOTIONS
Slide 9
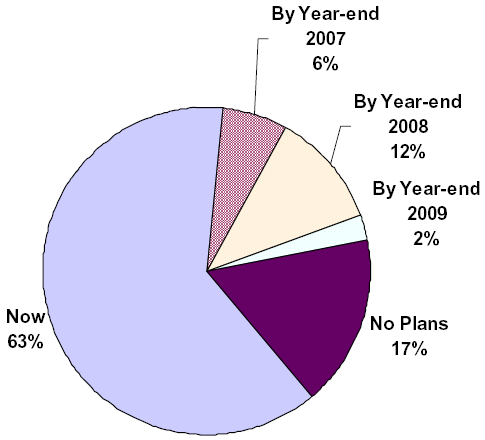
Members Offering Video Service
Slide 10
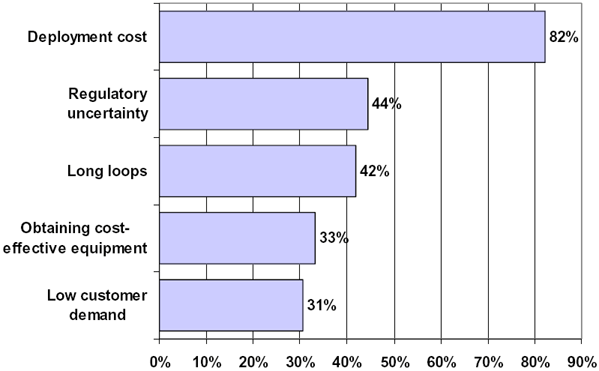
BARRIERS TO BROADBAND DEPLOYMENT
Slide 11
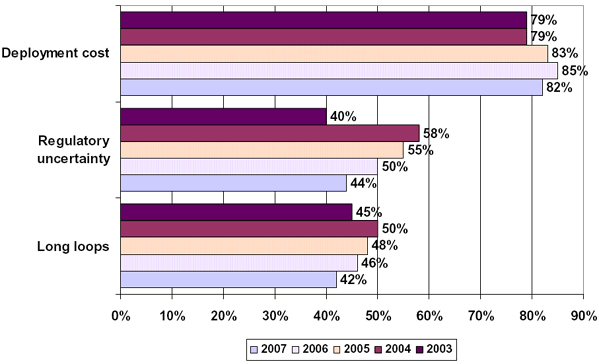
BARRIERS TO BROADBAND DEPLOYMENT: 2003-2007
Slide 12
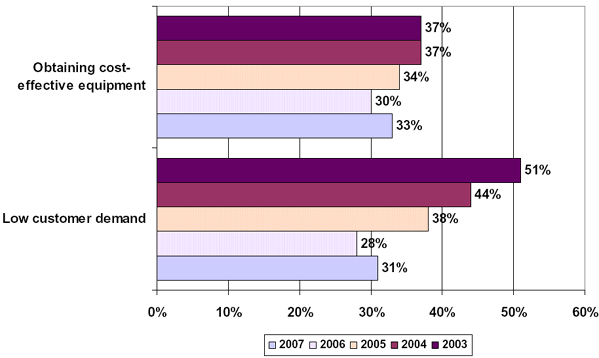
BARRIERS TO BROADBAND DEPLOYMENT: 2003-2007 (con’t.)
Slide 13
Key Issues
- Universal Service
- Access to video content
- Compensation for use of the network
- Regulatory certainty
- Unfunded mandates

 U.S. Department
of Justice
U.S. Department
of Justice