Government Exhibit P4875
LAN010531003-18001-824

CONFIDENTIAL
JD Edwards Product Market
Strategy: Making it Actionable

Discussion document
May 31, 2001
This report is solely for the use of client personnel. No part of it may be circulated, quoted, or reproduced for distribution outside the client organization without prior written approval from McKinsey & Company. This material was used by McKinsey & Company during an oral presentation; it is not a complete record of the discussion.
JDEC-01-030440
SUMMARY OF TODAY'S DISCUSSION
- In our last discussion, we recommended that JD Edwards aggressively focus on their historical core mid-market business segments to become a $2.5 billion-4.5 billion company by 2005
- To reach this target, JD Edwards should further focus within the core, create a compelling marketing plan, and reallocate and improve productivity of resources
- JD Edwards should further focus on "sweet spot" accounts in specific business segments/verticals within the $500 million-3 billion range to focus JD Edwards' constrained resource pool
- JD Edwards should then create a compelling marketing plan targeted at these verticals, including value propositions, product and service bundles, and appropriate marketing vehicles
- JD Edwards should then use these marketing programs to reallocate sales, product development and consulting resources to align against the opportunity, as well as improve productivity to achieve a competitive cost structure
- To execute this strategy, JD Edwards should develop detailed action plans and begin executing across marketing, product development, sales, and consulting
JDEC-01-030441
LAST DISCUSSION, WE RECOMMENDED THAT JD EDWARDS FOCUS AGGRESSIVELY ON ITS HISTORICAL CORE MID-MARKET BUSINESS SEGMENTS
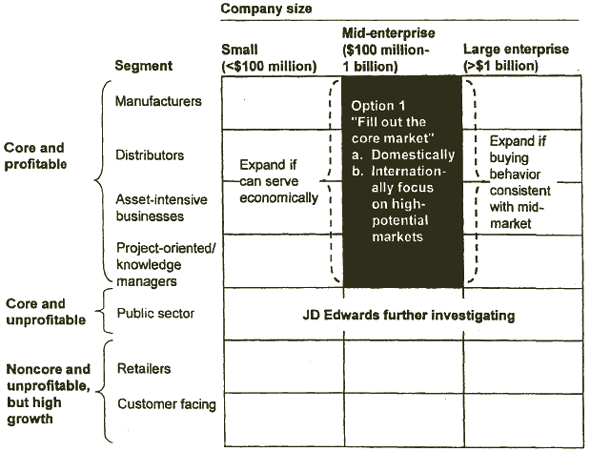 [D] [D]
Source: JDE financial data; McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030442
| FOCUSING ON THESE SEGMENTS COULD RESULT IN REVENUES BETWEEN $2.5 BILLION AND 4.5 BILLION BY 2005 |
 |
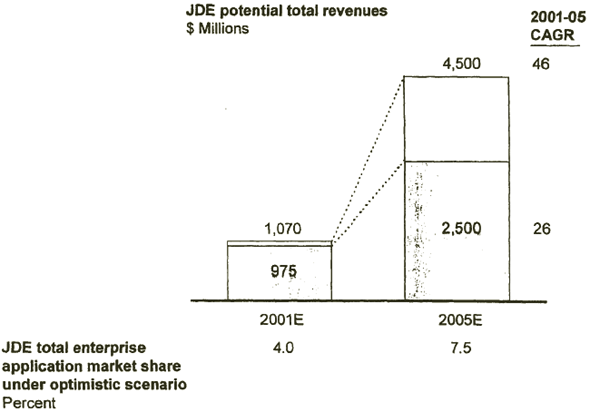 [D] [D]
Source: JD Edwards financials; customer interviews; McKinsey interviews; AMR; McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030443
SINCE OUR LAST DISCUSSION, WE FOCUSED ON THREE ISSUES
- Further define JD Edwards core mid-market "sweet spot" in terms of company size and target verticals
- Frame necessary changes to marketing, including value proposition, product/service bundles and pricing
- Define the implications for resources, skills, and productivity required for
- Sales
- Product development
- Consulting
JDEC-01-030444
SUMMARY OF TODAY'S DISCUSSION
- In our last discussion, we recommended that JD Edwards aggressively focus on their historical core mid-market business segments to become a $2.5 billion-4.5 billion company by 2005
- To reach this target, JD Edwards should further focus within the core, create a compelling marketing plan, and reallocate and improve productivity of resources
- JD Edwards should further focus on "sweet spot" accounts in specific business segments/verticals within the $500 million-3 billion range to focus JD Edwards' constrained resource pool
- JD Edwards should then create a compelling marketing plan targeted at these verticals, including value propositions, product and service bundles, and appropriate marketing vehicles
- JD Edwards should then use these marketing programs to reallocate sales, product development and consulting resources to align against the opportunity, as well as improve productivity to achieve a competitive cost structure
- To execute this strategy, JD Edwards should develop detailed action plans and begin executing across marketing, product development, sales, and consulting
JDEC-01-030445
JD EDWARDS MUST FURTHER FOCUS ITS DIRECT RESOURCES AS IT CANNOT COVER THE ENTIRE CORE MID-MARKET
Source: Dun & Bradstreet; McKinsey benchmarking
JDEC-01-030446
THERE ARE ADDITIONAL BENEFITS TO FOCUS
| |
Focus means... |
...which results |
| Sales |
- More targeted sales coverage
- Fewer segments verticals to know and sell to
- Simpler value proposition to sell
- Fewer relevant products to know and sell
- More proactive vs. reactive sales (e.g., named accounts)
|
- Increased efficiency
- Simple, more efficient training
- Higher win/loss ratio
- Increased sales
- More effective, skilled sales people
- Higher prices (fewer competitive RFPs)
|
| |
| Marketing |
- Simpler, easier to understand marketing messages (i.e., one value proposition)
- More focused marketing spend across fewer verticals
|
- Increased sales
- Higher overall brand awareness
- Increased effectiveness of targeted marketing dollars
|
| |
| Product development |
- Fewer vertical-specific products to develop
- Less customization required given single mid-market value proposition
- Less QA, given similar problems across customers
|
- Increased efficiency and sales
- Products with a better feature/functionality match
- Increased investment in new product development with redeployed resources
- Faster time to market
|
| |
| Consulting |
- More targeted consulting coverage
- Fewer segments/verticals to learn
- Fewer products to know
- Simpler value proposition to learn and sell
- Single set of similar business partners
|
- Increased efficiency
- Simple, more efficient training
- Higher utilization, less ramp up time
- Increased sales
|

JDEC-01-030447
| TO ACHIEVE THIS FOCUS, JD EDWARDS MUST DETERMINE ITS CORE MID-MARKET SWEET SPOT |
ILLUSTRATIVE |
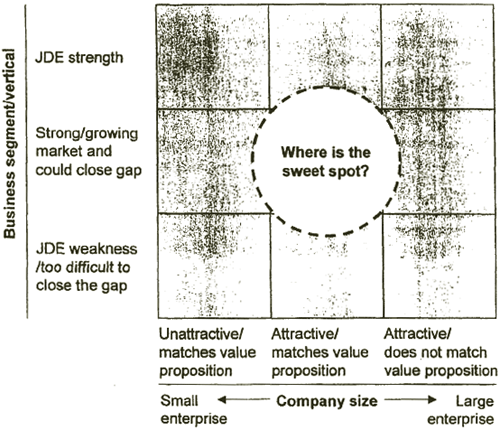
[D]
|
 |
Criteria to determine the sweet spot
- Business segment/vertical
- JDE market share
- JDE fit with segment functionality requirements
- JDE ability to close functional gap
- 2005 market size and growth
- Customer size
- Buying behavior
- Average deal size
- Gross margin
|
JDEC-01-030448
| JD EDWARDS SHOULD FOCUS ON HIGH POTENTIAL VERTICALS |
Focus |
| |
Business segment |
Vertical |
JDE share of market Percent |
2005 worldwide software market |
2000-02 CAGR Percent |
New product requirements |
Total 2005 software market Percent |
| JDE strong today |
Asset intensive |
Enery (oil exploration) |
23 |
13 |
-30 |
|
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Professional services |
19 |
470 |
39 |
|
|
| Asset-intensive |
Professional maintenance/repair services |
16 |
366 |
25 |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
Pharma/biotech |
16 |
327 |
12 |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
CPG |
13 |
278 |
0 |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
Primary fabricated materials (IFA) |
10 |
182 |
-14 |
|
|
| Asset-intensive |
Mining |
9 |
112 |
20 |
|
|
| Asset-intensive |
Construction |
9 |
234 |
39 |
|
|
| Distribution |
Electronics |
8 |
397 |
24 |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
Machinery |
5 |
393 |
-2 |
|
|
| Distribution |
Health care |
4 |
412 |
26 |
|
|
| Distribution |
CPG |
4 |
416 |
0 |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
Chemicals |
4 |
550 |
11 |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
Automotive/transportation |
4 |
473 |
2 |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
Paper products |
4 |
104 |
-10 |
|
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Construction |
3 |
234 |
39 |
|
|
| Distribution |
Automotive/transportation |
3 |
203 |
2 |
|
21 |
| Strong/ growing market and could close the gap |
Manufacturing |
Electronics |
2 |
3,207 |
24 |
Shop floor tracking, material requirement planning, design and project management |
|
| Distribution |
Transportation/warehousing |
1 |
2,708 |
41 |
Transportation planning and monitoring |
|
| Distribution |
Wholesale trade |
1 |
918 |
9 |
Transportation planning and monitoring |
|
| Distribution |
Telecom/cable/satellite |
1 |
594 |
54 |
|
|
| Asset-intensive |
Real Estate |
Unreadable |
Unreadable |
Unreadable |
|
|
| Asset-intensive |
Telecommunications |
0 |
5,537 |
54 |
Billing, KM, service provisioning |
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Defense contractors |
0 |
630 |
26 |
Project Management |
56 |
| JDE weakness/ too difficult to clost the gap |
Project-oriented/KM |
Medical devices |
2 |
71 |
18 |
|
|
| Asset-intensive |
Utilities |
1 |
622 |
11 |
Billing/provisioning |
|
| Manufacturing |
Apparel |
1 |
127 |
-7 |
Customer design/configuration tie-in to supply chain |
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Textiles |
1 |
630 |
-5 |
|
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Education |
0 |
630 |
28 |
Student administration |
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Electronics |
0 |
1,603 |
24 |
Project management |
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Health services |
0 |
964 |
26 |
Insurance billing |
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Information providers |
0 |
728 |
18 |
KM content management |
|
| Project-oriented/KM |
Pharma/biotech |
0 |
327 |
12 |
Project management |
|
| Manufacturing |
Aerospace |
0 |
203 |
5 |
Project management |
23 |
Source: VSS & Interviews; McKinsey analysis; JDE financials
JDEC-01-030449
ON THE HIGH END, CUSTOMER BEHAVIOR SUGGESTS JD EDWARDS VALUE PROPOSITION IS LESS ATTRACTIVE WITH COMPANIES ABOVE $3 BILLION IN REVENUES

[D]
|
Examples of JD Edwards' large enterprise customers
- Dole Foods Company ($5 billion) - currently evaluating best-of-breed players for SCM, middleware, and information management software. Company strictly evaluates economics of software investment, including ROI and payback period
- LVMH ($12 billion) - key software needs in next 18 months include SCM, CRM, direct/indirect procurement, and middleware. Company leverages software to capture synergies between its 650+ subsidiaries
- Shell International Petroleum Company (>$75 billion) - strictly purchases software on best-of-breed basis and prefers customized integration. Believes JD Edwards current partnership strategy (e.g., Ariba, Siebel, and MicroStrategy) is attractive to large enterprise customers, but not mid-market
|
|
Source: Customer interviews
JDEC-01-030450
ONE CONSIDERATION FOR THE LOWER LIMIT IS PROFITABILITY AND DEAL SIZE


Although not a clean break, deals below $400 million-500 million tend to be smaller and therefore tend to be less profitable
|
 |
Source: Rolling Thunder, McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030451
| |
 |
|
| IN ADDITION, THERE IS SUFFICIENT OPPORTUNITY IN THE $500 MILLI0N-$3 BILLION RANGE TO FULLY FOCUS RESOURCES ON THESE SEGMENTS |
Sweet spot |
| |
 |
|
 [D] [D]
Source: Dun & Bradstreet, McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030452
| JD EDWARDS SHOULD FOCUS ON COMPANIES IN THE $500 MILLION-3 BILLION RANGE IN TARGET VERTICALS |
 |
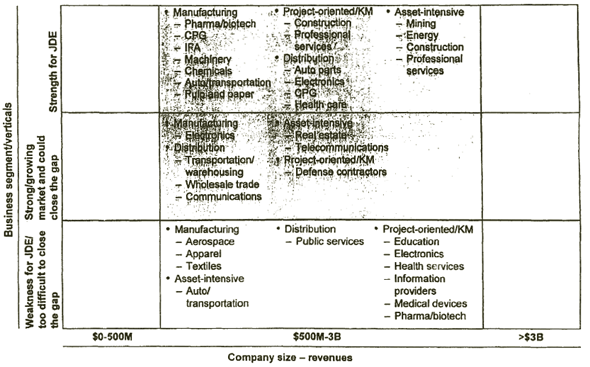 [D] [D]
JDEC-01-030453
SUMMARY OF TODAY'S DISCUSSION
- In our last discussion, we recommended that JD Edwards aggressively focus on their historical core mid-market business segments to become a $2.5 billion-4.5 billion company by 2005
- To reach this target, JD Edwards should further focus within the core, create a compelling marketing plan, and reallocate and improve productivity of resources
- JD Edwards should further focus on "sweet spot" accounts in specific business segments/verticals within the $500 million-3 billion range to focus JD Edwards constrained resource pool
- JD Edwards should then create a compelling marketing plan targeted at these verticals, including value propositions, product and service bundles and appropriate marketing vehicles
- JD Edwards should then use these marketing programs to reallocate sales, product development and consulting resources to align against the opportunity, as well as improve productivity to achieve a competitive cost structure
- To execute this strategy, JD Edwards should develop detailed action plans and begin executing across marketing, product development, sales, and consulting
JDEC-01-030454
MARKETING IMPLICATIONS
As competitors are aggressively targeting JD Edwards "sweet spot", JD Edwards must create a compelling marketing plan targeted at these segment verticals
- JD Edwards must understand the needs of each segment and vertical and develop a compelling value proposition to attract them
- JD Edwards must create appropriately priced product and service bundles to cater to each target segment and vertical
- JD Edwards must translate this into an actionable marketing plan to realize the revenue potential in target segments
JDEC-01-030455
| TOP TIER COMPETITORS ARE TARGETING JD EDWARDS "SWEET SPOT" WITH TAILORED MARKETING PLANS |
JDE target vertical |
| Competitor |
1999 ERP revenues in mid-market*
Percent |
Target business segments and verticals |
Mid-market buying behavior
|
| Functionality fit |
Integrated offering |
Low cost solutions |
| SAP |
53 |
All 4 core business segments, especially strong in
- Pharma/biotech
- Energy
- Electronics
- Auto/transportation
- CPG
- Chemicals
- Health care
|
|
- Preconfigured, industry-specific solutions in more than 50 verticals
|
- Fast Trak ERP - rapidly implemented, preconfigured solutions in ERP, SCM, procurement, and CRM
|
- Fixed price packages for software and services designed for mid-market
- Promote 40% lower cost and 30% less integration time than traditional solutions
- Delivery through a network of business partners and hosted solutions
|
| Oracle |
60 |
- Manufacturers, distributors, asset-intensive, retail, and public sector, especially strong in
- Energy
- Chemicals
- Electronics
- CPG
- Telecommunications
- Defense contractors
|
- Aerospace
- Utilities
- Education
- Financial services
|
- Software solutions designed for mid-market, including ERP, procurement, CRM, and SCM
|
Fast Forward solution provides bundled solution including software (ERP, SCM, CRM, and procurement), consulting, training, and maintenance |
Fast Forward solution model offers fixed-time, fixed-price solutions |
| PeopleSoft |
55 |
- Project-oriented/KM, public sector, manufacturers, and distributors, especially strong in
- Phama/biotech
- Auto/ transportation
- CPG
- Telecommunications
- Health care
|
- Utilities
- Financial services
- Education
|
- Full suite of software solutions for core verticals, including financial, HRMS, CRM, SCM. and procurement
|
- Accelerated Solutions designed specifically for companies between $100 million-500 million in revenues, including software (ERM, SCM, CRM, and procurement), consulting, training, and maintenance
- Preconfigured, package including hardware, software, operating system, and database
|
- Fixed-price solutions for companies between $100 million-500 million
|
* Mid-market defined as $30 million-1 billion
JDEC-01-030456
| JD EDWARDS SHOULD UNDERSTAND SEGMENT/VERTICAL NEEDS TO CRAFT A COMPELLING VALUE PROPOSITION |
EXAMPLE |
| |
Mid-market buying behavior
|
|
Potential value proposition to segment/vertical |
| 1. Feature/ functionality fit |
2. Integrated offering |
3. Low cost solutions |
| General manufacturer's value proposition |
- Primary needs
- Demand planning/ manufacturing
- Secondary needs
- Procurement
- Transportation management
- Warehouse management
- Business analysis
|
- Data must flow seamlessly between modules within ERP and other relevant modules
- Preference that products are developed by JDE or offer a seamless integration to own products
|
- Total cost of ownership is competitive
- Risk reduction through fixed price contracts
|
 |
"JD Edwards is the leading provider of manufacturing software offering a low-cost, low-risk integrated solution" |
| Specific vertical value proposition (CPG manufacturers) |
- Primary needs - manufacturing
-
- New product design/ development
- Material production planning/scheduling
- Discrete production (some process production)
- Secondary need - CRM
- Sales force automation
- Marketing automation
|
 Should not vary significantly by vertical Should not vary significantly by vertical |
 |
"JD Edwards knows the needs of mid-market CPG manufacturers better than any other ERP vendors" |
JDEC-01-030457
| JD EDWARDS SHOULD CREATE APROPRIATELY PRICED PRODUCT AND SERVICE BUNDLES |
EXAMPLE |
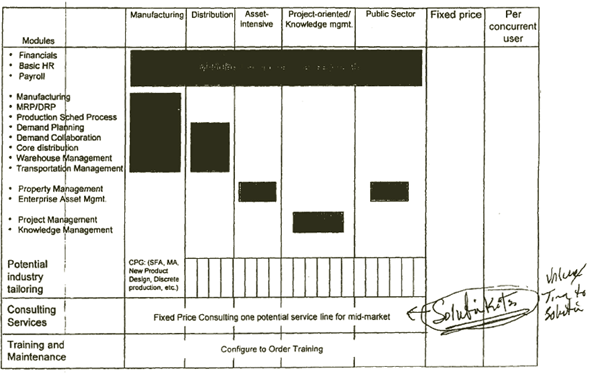 [D] [D]
JDEC-01-030458
| JD EDWARDS SHOULD TRANSLATE THIS INTO AN ACTIONABLE MARKETING PLAN |
EXAMPLE |
| |
Customer adoption life cycle - CPG manufacturing |
|
| Step 1 - generate awareness/interest |
Step 2 - drive initial purchase |
Step 3 - drive repeat purchase |
|
| Target audience |
- All key influences/ decision makers, including CEO level
|
- Primary - CTO/CIO
- Secondary - CFO, other business heads
|
- Primary - CTO/CIO
- Secondary-CFO, other business heads
|
| Marketing message |
- JD Edwards has a credible, proven history with CPG manufacturers
|
- JD Edwards can meet your specific feature/functionality requirements with a low cost, low risk integrated solution
|
- JD Edwards can seamlessly integrate additional functionality into your current ERP systems
|
| Marketing vehicle |
- Trade shows
- Industry seminars/ conferences
- Advertising through publications, Internet, etc.
- Sales collateral
- Special interest groups
- Direct mail
|
- Canned demos for unique CPG manufacturing needs
- Credible reference clients (e.g., 3 leading CPG manufacturers)
|
- Same as awareness vehicles plus
- Targeted collateral
- Targeted sales calls
- Telemarketing
|
JDEC-01-030459
SUMMARY OF TODAY'S DISCUSSION
- In our last discussion, we recommended that JD Edwards aggressively focus on their historical core mid-market business segments to become a $2.5 billion-4.5 billion company by 2005
- To reach this target, JD Edwards should further focus within the core, create a compelling marketing plan, and reallocate and improve productivity of resources
- JD Edwards should further focus on "sweet spot" accounts in specific business segments/verticals within the $500 million-3 billion range to focus JD Edwards' constrained resource pool
- JD Edwards should then create a compelling marketing plan targeted at these verticals, including value propositions, product and service bundles, and appropriate marketing vehicles
- JD Edwards should then use these marketing programs to reallocate sales, product development and consulting resources to align against the opportunity, as well as improve productivity to achieve a competitive cost structure
- To execute this strategy, JD Edwards should develop detailed action plans and begin executing across marketing, product development, sales, and consulting
JDEC-01-030460
SALES ORGANIZATION IMPLICATIONS
JD Edwards should alter its coverage model to capture the opportunity in the "sweet spot", and implement measures to improve overall productivity
- JD Edwards should focus and redeploy current AEs against opportunity in installed base and new "sweet spot" customers
- Independent of refocusing resources, JD Edwards should improve current productivity in-line with top-tier competitors
- Edwards should determine appropriate sales model, as future needs to migrate into smaller companies emerge
JDEC-01-030461
JD EDWARDS SHOULD REALIGN SALES RESOURCES AGAINST THE NEW OPPORTUNITY
 [D] [D]
JDEC-01-030462
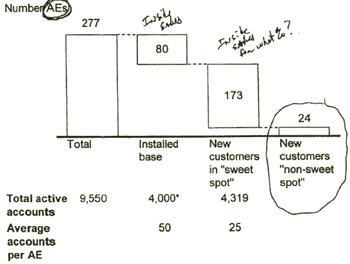
JD EDWARDS SHOULD ALLOCATE SALES RESOURCES FIRST TO CURRENT INSTALLED ACCOUNTS AND SECOND TO NEW ACCOUNTS IN THE SWEET SPOT
JD Edwards recommended sales allocation
** Includes government, not-for-profit, and other public services
Source: D&B, McKinsey Analysis
JDEC-01-030463
JD EDWARDS SHOULD IMPROVE CURRENT PRODUCTIVITY IN LINE WITH COMPETITORS
2000 total revenues/S&M costs
 [D] [D]
Source: Compustat
JDEC-01-030464
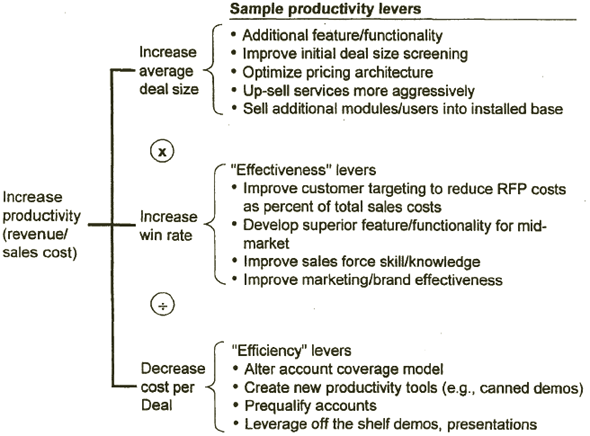
THERE ARE A NUMBER OF LEVERS TO IMPROVE SALES PRODUCTIVITY
JDEC-01-030465
JD EDWARDS SHOULD DETERMINE AN APPROPRIATE SALES MODEL, AS FUTURE NEEDS TO MIGRATES INTO THE LOWER-END EMERGE
Number of required new target companies to reach target
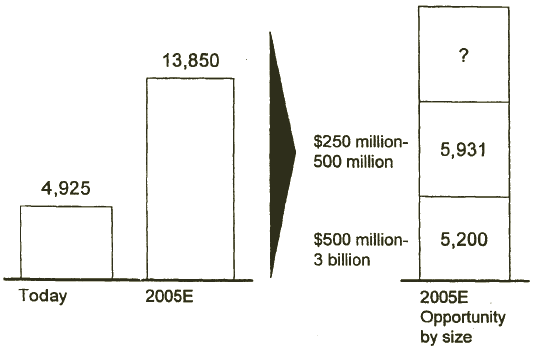
[D]
|
 |
- Where should JD Edwards get additional target customers - upstream or downstream?
- If JD Edwards migrate downstream, can you profitably serve through either a direct or indirect channel?
|
Source: D&B; McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030466
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IMPLICATIONS
JD Edwards is not currently spending enough on new product development to develop its future product pipeline and is potentially under-resourced. In order to solve this:
| |
1. |
JD Edwards may need to hire additional product development engineers to close the gap
|
 |
2. |
JD Edwards should reallocate resources to focus on core mid-market business segment needs (Handwritten checkmark next to this item)
|
| |
3. |
JD Edwards should determine how to free up QA/maintenance resources |
JDEC-01-030467
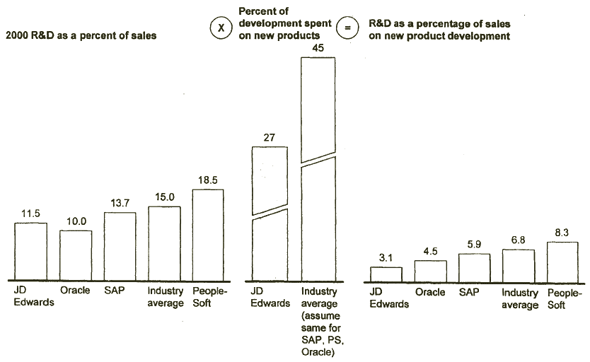
JD EDWARDS IS CURRENTLY UNDER RESOURCED VS. COMPETITORS AND IS NOT INVESTING ENOUGH IN NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
 [D] [D]
Source: Compustat; analyst reports; McKinsey benchmarking
JDEC-01-030468
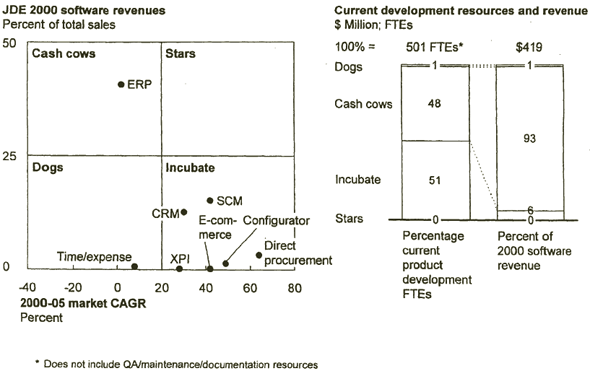
JD EDWARDS NEEDS TO EMPHASIZE NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT GIVEN THE CURRENT STATE OF THE PORTFOLIO
 [D] [D]
Source: AMR 2000; internal data; McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030469
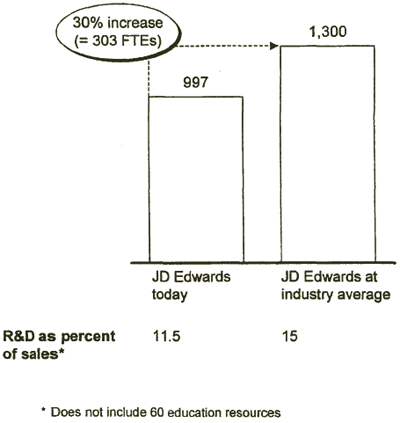
JD EDWARDS MAY HAVE TO INCREASE THE NUMBER OF PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT ENGINEERS
[D]
|
 |
- Should JD Edwards hire more engineers in the short term?
- How can additional capital be sourced to do this?
|
Source: Compustat, JD Edwards Internal Data
JDEC-01-030470
| STOPPING AND/OR REFOCUSING PROJECTS THAT ARE AIMED TOWARD NONCORE SEGMENTS WOULD FREE UP AN ADDITIONAL 76 FTES |
 |
| |
Rationale |
Recommended actions/number of FTEs |
Number of FTEs gained |
|
| Stop or move into maintenance mode |
Projects are outside core mid-market business segments and/or are commoditized for core markets |
- Eliminate Advanced Order Configurator (12)
 |
12 |
| Redeploy portion of resources to new product development |
Resources could be utilized more efficiently in other higher value areas |
- Outsource B9 strategic enhancement tools and redeploy 25% of resources (33 out of 132)
- Redeploy 50% of cross-industry applications (non-international component) (31 out of 62)
- Donut (24) - do you need best 24 people on Donut?
- Advanced Planning (95) - do you need 95 FTEs to develop a streamlined version of APS?
|
64
 |
| Refocus the project |
>Project is currently targeting large enterprise; refocus efforts to develop functionality that meets mid-market needs |
- Refocus advanced Planning (95)/Supply Chain Execution (13)
- Refocus XPI applications (42)
- Refocus Donut (24)
|
0 |
Source: JD Edwards Product Development
JDEC-01-030471
JD EDWARDS SHOULD DETERMINE HOW TO FREE UP QA/MAINTENANCE RESOURCES
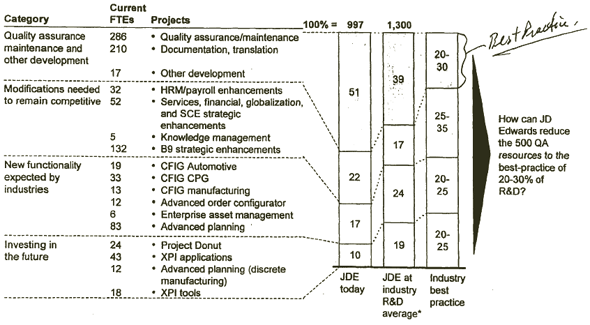 [D] [D]
Source: McKinsey analysis; JD Edwards internal data/interviews
JDEC-01-030472
JD EDWARDS SHOULD DETERMINE HOW TO FREE UP QA/MAINTENANCE RESOURCES WHILE MEETING QUALITY DEMANDS
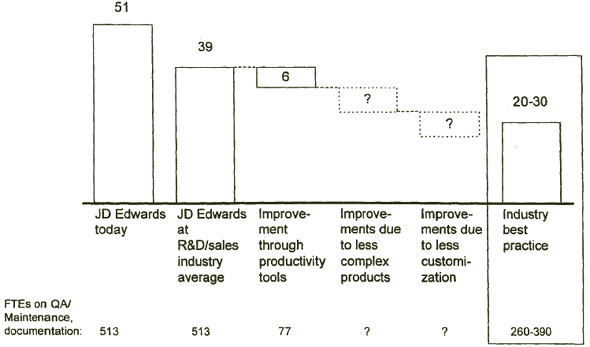 [D] [D]
Source: JD Edwards internal data;McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030473
CONSULTING IMPLICATIONS
To capture the opportunity in the core mid-market segments, JD Edwards should realign and retrain resources in the short term, while ultimately improving productivity
- JD Edwards should realign resources against the mid-market opportunity as the sales force pulls demand
- JD Edwards should retrain current consulting resources to meet "sweet spot" consulting needs
- JD Edwards should improve productivity, potentially through realization, utilization, and price levers
JDEC-01-030474
AS JD EDWARDS REFOCUSES ON THE SWEET SPOT, CONSULTING REALIGNMENT WILL FOLLOW NATURALLY
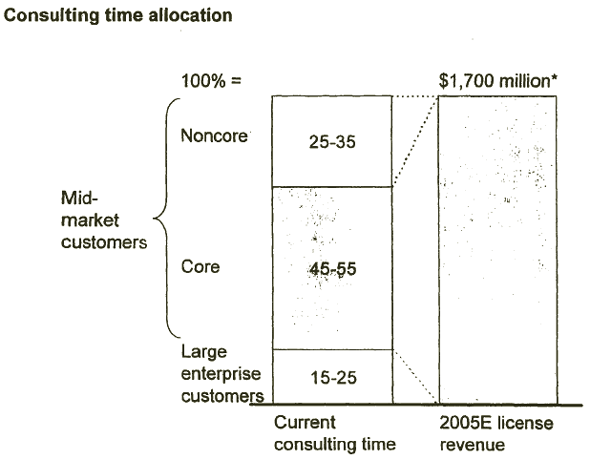 [D] [D]
Source: JD Edwards interviews; McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030475
CONSULTING WILL NEED NEW SKILLS TO EFFECTIVELY SERVE SWEET SPOT SEGMENTS
| Mid-market need |
Explanation |
Current JDE performance |
Competitor performance |
| Targeted vertical expertise/ understanding |
Understanding of targeted "sweet spot" business needs is critical to successful mid-market offering
 |
 |
- JDE consultants/managers have sound experience with "sweet spot" verticals, with strongest presence in
- Manufacturing
- Distribution
- Managers often do not know JDE product well enough to manage high-quality installation
|
 |
- Customers do not cite any competitors they prefer over JDE
|
| Cross-trained technical skill |
- Application consultants should be cross-trained in multiple applications to limit cost and number of consultants
- Technical programmers should be deeply experienced in IT architecture design so solutions can be developed by single resource
|
 |
- Applications consultants are generally trained in 1 application
- Technical consultant skill also not broad enough for single resource
|
 |
- Skill sets are fragmented across software vendors, big 5, and local service providers
|
| Project Management |
- Potential need for fixed price contract increases importance of strong project management
|
 |
- Project manager is not as skilled as needed on managing scope, costs, and technical challenge
|
 |
- While SAP and Oracle have adequate project management skills, the management layer is often too large and expensive
- Big 5 have strong project management skills across technical and nontechnical dimensions but customer prefers vendor management
|
JDEC-01-030476
JD EDWARDS SHOULD ALSO IMPROVE CONSULTING PRODUCTIVITY
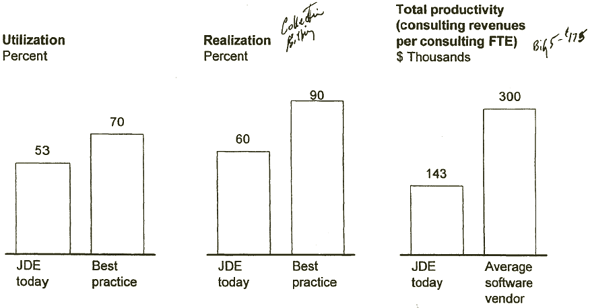 [D] [D]
Source: JD Edwards financials; McKinsey best practices
JDEC-01-030477
PRODUCTIVITY CAN BE INCREASED BY PULLING ANY OF 3 LEVERS

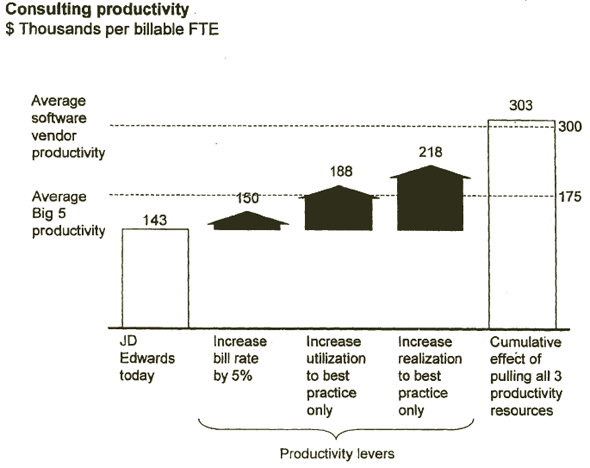 [D] [D]
Source: McKinsey analysis; Web site
JDEC-01-030478
IF PRODUCTIVITY IS IMPROVED, FEWER RESOURCES THAN TODAY MAY BE NEEDED
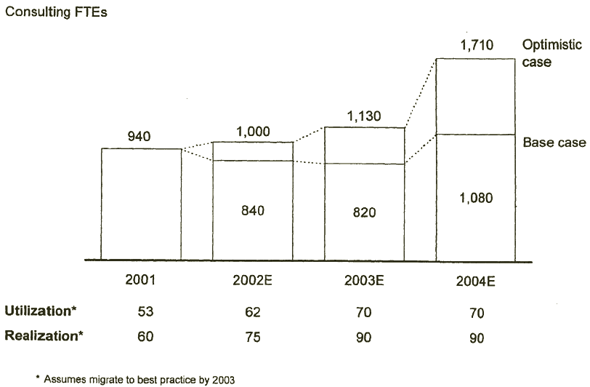 [D] [D]
Source: McKinsey analysis
JDEC-01-030479
SUMMARY OF TODAY'S DISCUSSION
- In our last discussion, we recommended that JD Edwards aggressively focus on their historical core mid-market business segments to become a $2.5 billion-4.5 billion company by 2005
- To reach this target, JD Edwards should further focus within the core, create a compelling marketing plan, and reallocate and improve productivity of resources
- JD Edwards should further focus on "sweet spot" accounts in specific business segments/verticals within the $500 million-3 billion range to focus JD Edwards' constrained resource pool
- JD Edwards should then create a compelling marketing plan targeted at these verticals, including value propositions, product and service bundles, and appropriate marketing vehicles
- JD Edwards should then use these marketing programs to reallocate sales, product development and consulting resources to align against the opportunity, as well as improve productivity to achieve a competitive cost structure
- To execute this strategy, JD Edwards should develop detailed action plans and begin executing across marketing, product development, sales, and consulting
JDEC-01-030480
| JD EDWARDS MUST EXECUTE TARGETED INITIATIVES TO CAPTURE THE OPPORTUNITY IN CORE SEGMENTS |
FOR DISCUSSION |
 [D] [D]
JDEC-01-030481
JD EDWARDS MUST EXECUTE TARGETED INITIATIVES TO CAPTURE THE OPPORTUNITY
| |
Step 1
Develop detailed strategy
|
Step 2
Develop action plan
|
Step 3
Execute
|
| |
|
| Develop and launch targeted product/market programs |
- Develop detailed product marketing strategies (SCM, CRM, One World, ERP)
- Target customer
- Value proposition
- Feature/functionality
- Pricing strategy
- Communication program
- Channel strategy
- Develop overall customer management program (e.g., size of opportunity, tools, ROI)
- Determine optimal approach to close product/market gaps
- build internally, acquisitions, partnerships
|
- Develop detailed action plans by function
- Product development
- Channel marketing
- Sales (training, collateral)
- External communication plan (audience, message, vehicle)
- Develop communication tools/materials
- Implement and train on new customer management system
|
- Implement action plan
- Distribute communication plan
- Implement training program
|
| Reinvent sales model for core mid market |
- Develop short term coverage model
- Assess skill gaps
- Verticals/segments
- Product
- Selling skills
- Assess current sales process vs. customer needs and segment profitability
- Resources
- Demos
- Qualification
|
- Develop account plan
- Design training program
- Design new sales models that meet needs and profitability requirements for different segments
|
- Execute plan
- Execute training program
- Pilot, refine and rollout
|
JDEC-01-030482
JD EDWARDS MUST EXECUTE TARGETED INITIATIVES TO CAPTURE THE OPPORTUNITY (continued)
| |
Step 1
Develop detailed strategy
|
Step 2
Develop action plan
|
Step 3
Execute
|
| |
|
| Develop a deploy a new consulting model |
- Develop consulting model to meet target customer needs (TCO, skills/timelines, partners)
- Assess skills gaps to meet mid market consulting needs
- Re-evaluate current consulting partnerships
|
- Develop detailed action plan
- Resource allocation
- Training
|
|
| Aggressively enter into new international markets |
- Develop a detailed strategy for each target country (products, customer segments, partners strategy, customer support)
- Develop exit strategy for countries to divest
|
- Assess localizaton requirements
- Develop country-specific action plans
- Sales strategies/account plans
- Marketing programs
- Consulting plan
- Product localization plans
|
|
| Technical Support |
- Assess technology support needsn for mid market
- Assess skill gaps to execute against mid market needs
|
- Develop training programs for new customer management system
|
- Roll-out program to train technical consultants
|
|

 U.S. Department
of Justice
U.S. Department
of Justice















 Should not vary significantly by vertical
Should not vary significantly by vertical